What Does UTI Discharge Look Like (With Pictures)?
Our content is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice by your doctor. Use for informational purposes only.
A urethral discharge is a term that describes abnormal secretions (mucous, pus, watery, or bloody) that comes out SPONTANEOUSLY from the urethral opening (without urination).
The most common form of urinary tract infection is cystitis (infection of the urinary bladder). This type of UTI, predominant in women, typically doesn’t lead to urethral discharge.
In This article. You will learn the different types of UTIs and the common causes of urethral discharge.
Quick insights:
- UTI does not typically cause urethral discharge but cloudy urine (in some cases)
- Urethritis discharge may look like pus, mucus, or water
- Cystitis (bladder infection) and pyelonephritis (kidney infection) typically don’t cause spontaneous discharge
- Cystitis or pyelonephritis may cause turbid (cloudy) or bloody (reddish urine), or blood clots in urine
- Urethritis is an inflammation limited to the urethra that typically causes the spontaneous discharge.
- Most cases of urethritis are due to sexually transmitted infections
- Gonorrhea Urethritis (UTI) discharge typically looks like yellowish or grayish pus (purulent).
- Non-gonorrheal urethritis discharge may look clear and white. It may be thick as mucus or watery.
- Symptoms that warrant seeing a doctor include severe unexplained burning sensation in the urethra, inflamed or swollen urethral opening, fever, genital ulcers, cloudy or turbid urine, abnormal vaginal secretions, vaginal or urethral itching, bloody urethral discharge, bloody urine, or blood clots in urine.
[1] Does UTI Cause Discharge?
UTI (urinary tract infection) is a broad term that describes infections affecting any part of the urinary system. Common forms and urinary tract infection and their relation to urethral discharge:
| TYPE OF UTI | FEATURES | URETHRAL DISCHARGE |
|---|---|---|
| Urinary bladder (cystitis) | – The most common form of UTI. – Occurs mainly in females. – Frequent painful urination. – Bladder pressure. – It may lead to cloudy or bloody urine. |
No |
| Kidney (pyelonephritis) | – Less common – Same symptoms of cystitis plus: fever, flank pain, and other systemic symptoms |
No |
| Urethra (urethritis) | Often due to sexually-transmitted diseases. – the most common causes of UTI discharge. |
Common |
- Occurs mainly in females.
- Frequent painful urination.
- Bladder pressure.
- It may lead to cloudy or bloody urine. | No | | Kidney (pyelonephritis) | – Less common
- Same symptoms of cystitis plus: fever, flank pain, and other systemic symptoms | No | | Urethra (urethritis) | Often due to sexually-transmitted diseases.
- The most common causes of UTI discharge. | Common |
So, the common types of UTI (cystitis and pyelonephritis) don’t lead to discharge (spontaneous secretions from the urethra without urination). But they may cause turbid (cloudy) or bloody (reddish urine), or blood clots in urine.
[2] What does UTI Urine (cystitis and pyelonephritis) look like?
As the above table explains, the classic UTI affecting the bladder and/or the kidneys typically doesn’t cause spontaneous discharge. Likewise, most cases of cystitis don’t lead to visible changes in urine color or clarity.
However, some cases of cystitis (bladder infection) or pyelonephritis (kidney infection) may cause either:
- Turbid (cloudy) urine: Severe cases may make you pee very turbid urine looking like pus (purulent discharge). Purulent or turbid urine comes out when you pee (it doesn’t come out spontaneously).
- Bloody urine: many UTIs may present with pink or reddish urine due to blood in the urine.
- Blood clots in urine: Severe UTI cases may rarely present with small or large blood clots in urine.
[3] Urethritis discharge: Causes and what does it look like?
Urethritis is an inflammation limited to the urethra. It is more common in males. However, it may also occur in females (often associated with vaginitis or cervicitis).
Urethritis is a special form of UTI that typically affects the urethra (the tube connecting the urinary bladder to the outside of the body).
Most cases of urethritis are due to Sexually-transmitted infections (STIs).
Causes:
The most common causes of urethritis include (reference):
- Neisseria gonorrhea: the leading cause of urethritis. It is a sexually-transmitted disease.
- Chlamydia Trachomatis: the most common non-gonococcal cause of urethritis.
- Tricholoma vaginalis (a protozoal infection).
- Herpes simplex virus urethritis.
- Adenovirus.
- H. influenza bacteria.
- Candida species (fungal infection) and others.
- Chemical irritations, as with soap and urethral irritation.
What does urethritis UTI discharge look like?
Here are what urethritis discharge looks like:
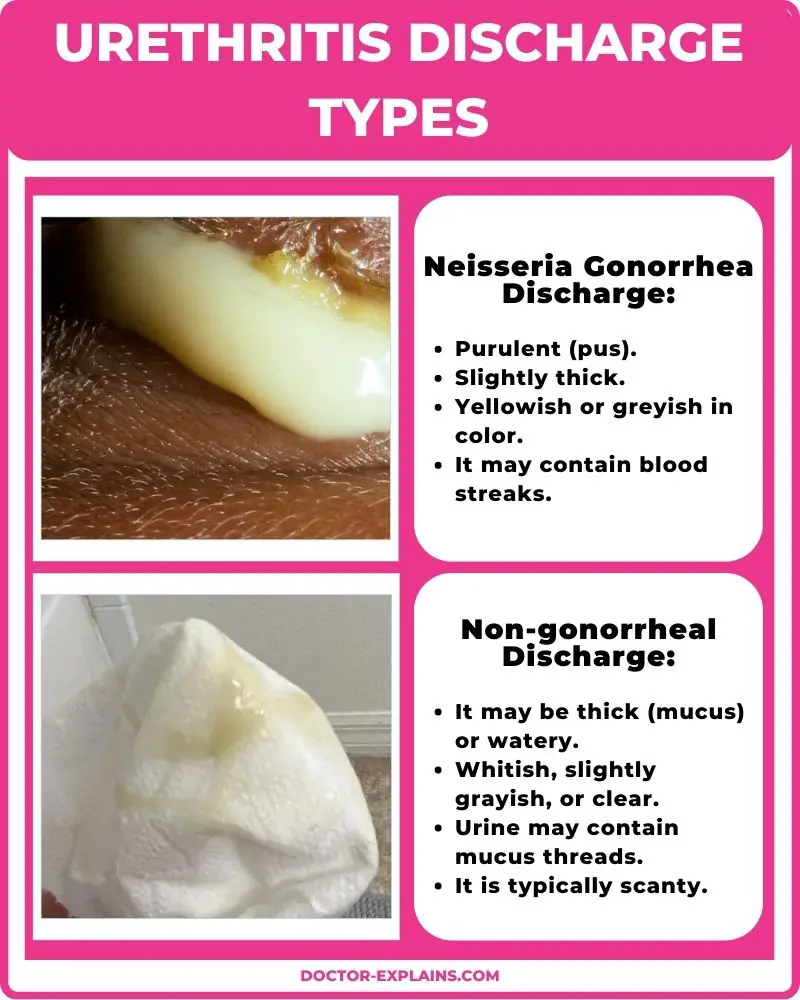
- In urethritis due to Neisseria gonorrhea (the most common cause of urethritis):
- It typically affects men.
- The period between getting infected and symptoms are typically 2-5 days.
- Rapid onset.
- Spontaneous discharge looks like pus (purulent) which is yellowish or grayish milky fluid.
- In Women, it may typically cause cervicitis (cervix infection). Symptomatic cases present with dysuria and mucus and purulent (mucopurulent discharge).
- In Urethritis due to Chlamydia trachomatis:
- It is the second most common cause of urethritis.
- The period between getting infected and the appearance of symptoms is longer (7-14 days).
- Most patients with chlamydia have pain during urination (dysuria) without discharge.
- Chlamydia urethritis discharge typically looks white, grey, or even clear (in contrast to the purulent discharge of Neisseria gonorrhea).
- The discharge is typically scanty and appears only in the morning and with stripping or milking of the urethra.
- In women, most cases of chlamydia urethritis are associated with cervicitis (vaginal discharge, itching, vaginal bleeding, etc.). Also, many cases are asymptomatic.
- Other types of UTI urethritis:
- Herpes Simplex virus urethritis commonly causes urethritis with severe urethral pain and genital ulcers. However, the discharge is less common and is typically similar to chlamydia trachomatis.
- Other non-gonococcal urethritis typically presents with whitish clear discharge.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
The type (mucous or watery) and color (whitish, greyish, or yellowish) of urethral discharge are not characteristic and cannot be used to diagnose the cause of UTI or urethritis.
Moreover, many cases of urethritis are caused by more than one organism (e.g., chlamydia and Neisseria gonorrhea infection occur simultaneously in many cases). So, the discharge typically serves as a sign of urethritis rather than a clue to the cause.
To diagnose the cause, your doctor must perform some microbiological and microscopic tests.
[4] When to see a doctor.
Any abnormal discharge from the urethra (regardless of the presence of other symptoms) should be investigated by your doctor.
Plan a visit to your GP or infectious disease specialist if you have spontaneous urethral discharge (watery, purulent, or mucus-like). Also, see a doctor if you have:
- Severe unexplained burning sensation in the urethra (with or without urination).
- Inflamed or swollen urethral opening.
- Fever.
- Genial ulcers.
- Cloudy or turbid urine.
- Abnormal vaginal secretions
- Vaginal or urethral itching.
- Bloody urethral discharge, bloody urine, or blood clots in urine.
- Evidence-based
- Written by a doctor.
MD, Internal Medicine and Nephrology specialist.

Dr. Esraa A. MagidAuthor
MORE INSIGHTS